Articles in the SQL category
PostgreSQL continuous backups are very powerful, if you know how to use them for recovery. There’s nothing else to do to be sure about that other than actually trying it. Personally, I see recovery as a single process with two possibly different outcomes:
- you’re recovering to the same state your cluster is/was in (because of a hardware failure, provider switch, …) - it’s more of a data migration, but you need your backup anyway
- you’re doing a point-in-time-recovery (someone dropped the wrong table, data got corrupted, …)
Both scenarios follow the same steps and differ slighty at the end.
- Stop the PostgreSQL cluster.
- Copy the current
PGDATA_DIR somewhere safe, just in case you screw up.
- Replace the
PGDATA_DIR with the full backup. If you start the cluster right away, it will boot to the last full backup state (in my case, missing a week of WAL segments tops).
General recovery
In this case, you’re trying to recover as far as possible. With previous steps done succesfully, the next follow:
- Copy all archived WAL segments created after the last full backup to
PGDATA_DIR/pg_xlog. These can be found with find -newer command run against the corresponding .backup file in your wal-archive/u/p directory.
- If your full backup strategy includes
recovery.conf file creation, you cane safely move it or remove it.
- Start the database cluster again. It is going to boot to the last working state.
If you’re about to migrate your data, you might be better off with simple pg_dump, pg_dumpall and pg_restore commands rather than using full backup/WAL segments combination.
Point-in-time-recovery
PostgreSQL’s PITR can help you restore your accidentally deleted/corrupted data. After the first three steps mentioned above, you should follow with these:
- Copy all archived segments created after the last full backup somewhere the PostgreSQL user can read them (
/your-wal-recovery-folder/ for example).
- Set up the
recovery.conf file properly. If you know something nasty happened at 2018-01-29 08:00:00, try to recover right to that point (or to any other, as described in the documentation).
restore_command = 'cp /your-wal-recovery-folder/%f "%p"'
recovery_target_time = '2018-01-29 08:00:00'
- Start the database cluster again. It is going to boot to the last full backup and then play all the WAL segments until the recovery target. Depending on how many WAL segments are about to be used, this might take a while.
Pitfalls
You don’t want to find yourself in the middle of the biggest database failure of the century just to find out your backups don’t work, and even if they did, you would have no idea how to use them. Or, even worse, there are no backups at all, because your backup strategy has been failing silently without a single notice for several months.
Tips
Try to recover from your backups once in a while.
I forget things and make mistakes. We all do. That’s why I built an ensemble that takes care of our database automatically. Nothing fancy, just a bunch of good old Bash scripts managed with systemd rathern than cron. Next time, I’d like to show you the code and walk you through our current setup.
Just a very few of my day-to-day work tasks can be accomplished without PostgreSQL. For years I’ve been a (power) user of this wonderful relational database, knowing almost nothing about how its internals really work. Faced with the need to build a backup and recovery strategy, I’ve recently read up a lot on this topic.
As I don’t find it very odd for a GIS person to be given such an extraordinary task (nobody wants to lose the priceless spatial data, right?), I hope this series might shed light on how to prepare and manage the backup/recovery process to those, who are up to such a task. I won’t be discussing backup strategies based on pg_backup tool, as those don’t offer neither continuous archivation, nor point-in-time-recovery (PITR) - those two features disqualifies it as CleverMaps production backup strategy.
That leaves us with taking periodic base backups combined with continuous WAL archivation, as described below.
Taking base backups
Archived WAL segments are worthless without a base backup they can be run on. It’s crucial to have consistent, periodic base backups to keep your data safe.
pg_basebackup takes base backup of PostgreSQL cluster. Nothing fancy. Gzipping the output folder once the backup is done is definitely a good idea.
pg_basebackup \
--pgdata=/mnt/backup/base/backup_number \
--format=plain \
--write-recovery-conf \
--xlog-method=stream \
--label=${CR_LABEL} \
--checkpoint=fast \
--progress \
--verbose
In our current environment, we take a base backup of each of our clusters once a week.
WAL archiving configuration
To properly set WAL archiving, several postgresql.conf settings has to be adjusted:
wal_level = replicaarchive_mode = onarchive_command = test ! -f /backup/wal/%f && cp %p /backup/wal/%f
Setting wal_level to replica writes enough information for WAL archiving. Turning on archive_mode will run archive_command each time a WAL segment is completed. archive_command might be anything from simple cp to rsync or aws s3 cp commands. It is absolutely critical that the command returns non-zero exit code in case of failure (including when a file with the same name already exists in your backup folder).
That’s it, after reloading PostgreSQL service, new WAL files should be copied to /backup/wal directory. The PostgreSQL process user (postgres usually) has to be able to write to the location.
Pitfalls
- If
archive_command fails, WAL segment remains on your database drive. If it keeps failing long enough, you’ll run out of space and the database will crash.
- If the backup location fills up, the above-mentioned happens as well.
- If you lose or corrupt any of the archived WAL segments, you won’t be able to pass through. That’s why you want to be sure that your
archive_command actually does what you think it does.
Tips
It might be a real PITA (fiddling around WAL segments included) to start a crashed database cluster with no space left. Keeping a dummy file in your pg_xlog location might save you a lot of trouble. Create one with following command. If you run out of space, remove this file and you get 300 MB for free. Don’t forget to recreate it after you start the cluster.
dd if=/dev/zero of=/path_to_your_database_cluster/pg_xlog/DO_NOT_MOVE_THIS_FILE bs=1MB count=300
There’s no need to keep archived WAL segments forever. They’re only needed until you take another base backup. Again, deleting WAL segments manually (or using find ! -newer previous_base_backup.tar.gz) might lead to accidental corruption of your backups. It’s much safer to use pg_archivecleanup pointed to your WAL backup folder, referencing the last sucessful full backup. Below is the script we use to keep our WAL backup folder of reasonable size, keeping the last three full backups.
# Find base_backup files not older than 3 weeks
# Sort by date
# Use the oldest one as a reference
OLDEST_BASE_BACKUP=$(basename $(find ${CR_WAL_BACKUP_DIR}/u/p/ -type f -iname "*.backup" -mtime -21 -print0 | \
xargs -0 ls -t | \
tail -n 1))
# Find all subfolders
# Except the u/p backup subfolder
# Execute pg_archivecleanup for each of the subfolders
find $CR_WAL_BACKUP_DIR \
-type d \
-not -path "${CR_WAL_BACKUP_DIR}u*" \
-exec pg_archivecleanup -d {} $OLDEST_BASE_BACKUP \;
Functional backups are crucial part of a solid backup/recovery system. They’re still just one half of that system, though. If not tested thoroughly, they’re even less than that. More on testing backups and recovering from failures next time.
Since version 2.4.0, PostGIS can serve MVT data directly. MVT returning queries put heavy workload on the database though. On top of that, each of the query has to be run again every time a client demands the data. This leaves us with plenty of room to optimize the process.
During the last week, while working on the Czech legislative election data visualization, I’ve struggled with the server becoming unresponsive far too often due to the issues mentioned above.
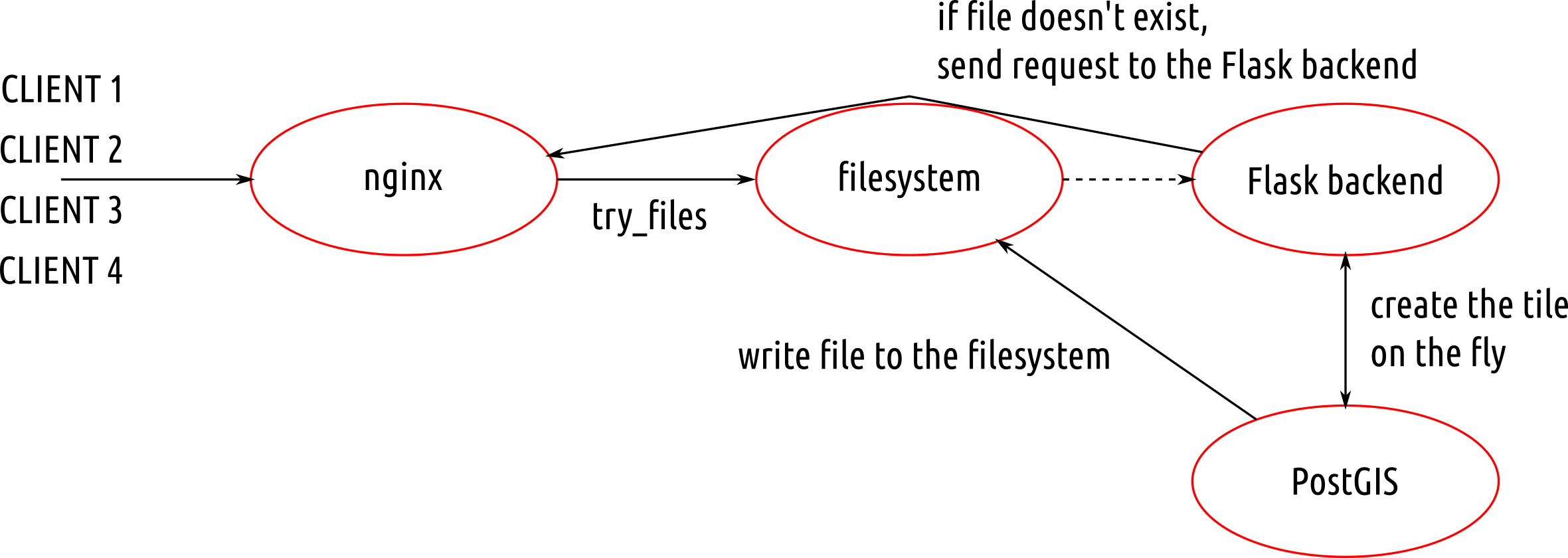
According to the schema, the first client to come to the server:
- goes through filesystem unstopped, because there are no cached files yet,
- continues to the Flask backend and asks for a file at
{z}/{x}/{y},
- Flask backend asks the database to return the MVT for the given tile,
- Flask backend writes the response to the filesystem and sends it to the client.
Other clients get tiles directly from the filesystem, leaving the database at ease.
Nginx
Nginx is fairly simple to set up, once you know what you’re doing. The /volby-2017/municipality/ location serves static MVT from the given alias directory. If not found, the request is passed to @postgis location, that asks the Flask backend for the response.
server election {
location /volby-2017/municipality {
alias /opt/volby-cz-2017/server/cache/;
try_files $uri @postgis;
}
location @postgis {
include uwsgi_params;
uwsgi_pass 127.0.0.1:5000;
}
}
Flask backend
Generating static MVT in advance
If you’re going to serve static tiles that don’t change often, it might be a good idea to use PostGIS to create files in advance and serve them with Nginx.
CREATE TABLE tiles (
x integer,
y integer,
z integer,
west numeric,
south numeric,
east numeric,
north numeric,
geom geometry(POLYGON, 3857)
);
Using mercantile, you can create the tiles table holding the bounding boxes of the tiles you need. PostGIS them inserts the actual MVT into the mvt table.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE tmp_tiles AS
SELECT
muni.muni_id,
prc.data,
ST_AsMVTGeom(
muni.geom,
TileBBox(z, x , y, 3857),
4096,
0,
false
) geom,
x,
y,
z
FROM muni
JOIN (
SELECT
x,
y,
z,
geom
FROM tiles
) bbox ON (ST_Intersects(muni.geom, bbox.geom))
JOIN party_results_cur prc ON (muni.muni_id = prc.muni_id);
CREATE TABLE mvt (mvt bytea, x integer, y integer, z integer);
DO
$$
DECLARE r record;
BEGIN
FOR r in SELECT DISTINCT x, y, z FROM tmp_tiles LOOP
INSERT INTO mvt
SELECT ST_AsMVT(q, 'municipality', 4096, 'geom'), r.x, r.y, r.z
FROM (
SELECT
muni_id,
data,
geom
FROM tmp_tiles
WHERE (x, y, z) = (r)
) q;
RAISE INFO '%', r;
END LOOP;
END;
$$;
Once filled, the table rows can be written to the filesystem with the simple piece of Python code.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import logging
import os
import time
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
CACHE_PATH="cache/"
e = create_engine('postgresql:///')
conn = e.connect()
sql=text("SELECT mvt, x, y, z FROM mvt")
query = conn.execute(sql)
data = query.cursor.fetchall()
for d in data:
cachefile = "{}/{}/{}/{}".format(CACHE_PATH, d[3], d[1], d[2])
print(cachefile)
if not os.path.exists("{}/{}/{}".format(CACHE_PATH, d[3], d[1])):
os.makedirs("{}/{}/{}".format(CACHE_PATH, d[3], d[1]))
with open(cachefile, "wb") as f:
f.write(bytes(d[0]))
Conclusion
PostGIS is a brilliant tool for generating Mapbox vector tiles. Combined with Python powered static file generator and Nginx, it seems to become the only tool needed to get you going.
Yesterday I spent two very unpleasant hours debugging the weirdest SQL error I’ve seen in my life, running the below query (simplified for this post).
psql -qAt --no-psqlrc <<BACKUP
DO
$$
DECLARE r record;
BEGIN
RAISE INFO '%', 'info';
END
$$;
BACKUP
Running this in your terminal will result in a nasty syntax error.
ERROR: syntax error at or near "1111"
LINE 2: 1111
^
ERROR: syntax error at or near "RAISE"
LINE 2: RAISE INFO '%', 'info';
^
ERROR: syntax error at or near "1111"
LINE 2: 1111;
You stare on the screen for a while, absolutely sure that number 1111 is nowhere close to the data you work with. You try again. Another error. You save the code into a file and try again. It works. What the heck? You try again using the bash heredoc. Another failure.
The minute you realize $$ is being substituted with the ID of the current process, you feel like the dumbest person on Earth. Yet the happiest one at the same time.
The solution is trivial.
psql -qAt --no-psqlrc <<BACKUP
DO
\$\$
DECLARE r record;
BEGIN
RAISE INFO '%', 'info';
END
\$\$;
BACKUP
I spend a lot of time reading PostgreSQL docs. It occurred to me just a few weeks ago that those versioned manuals are great opportunity to get an insight into PostgreSQL development history. Using PostgreSQL, of course.
TOP 5 functions with the most verbose docs in each version
SELECT
version,
string_agg(func, ' | ' ORDER BY letter_count DESC)
FROM (
SELECT
version,
func,
letter_count,
row_number() OVER (PARTITION BY version ORDER BY letter_count DESC)
FROM postgresql_development.data
) a
WHERE row_number <= 10
GROUP BY version
ORDER BY version DESC
Seems like a huge comeback for CREATE TABLE.
| VERSION |
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
5th |
| 10.0 |
CREATE TABLE |
ALTER TABLE |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
SELECT |
| 9.6 |
REVOKE |
ALTER TABLE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
SELECT |
| 9.5 |
REVOKE |
ALTER TABLE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
SELECT |
| 9.4 |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
ALTER TABLE |
CREATE TABLE |
SELECT |
| 9.3 |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
ALTER TABLE |
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES |
| 9.2 |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
ALTER TABLE |
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES |
| 9.1 |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
ALTER TABLE |
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES |
| 9.0 |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
ALTER TABLE |
ALTER DEFAULT PRIVILEGES |
| 8.4 |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
CREATE TABLE |
ALTER TABLE |
SELECT |
| 8.3 |
REVOKE |
CREATE TABLE |
GRANT |
ALTER TABLE |
COMMENT |
| 8.2 |
REVOKE |
CREATE TABLE |
GRANT |
ALTER TABLE |
SELECT |
| 8.1 |
REVOKE |
CREATE TABLE |
GRANT |
ALTER TABLE |
SELECT |
| 8 |
CREATE TABLE |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
SELECT |
ALTER TABLE |
| 7.4 |
CREATE TABLE |
REVOKE |
ALTER TABLE |
GRANT |
SELECT |
| 7.3 |
CREATE TABLE |
SELECT |
ALTER TABLE |
REVOKE |
GRANT |
| 7.2 |
CREATE TABLE |
SELECT INTO |
SELECT |
ALTER TABLE |
CREATE TYPE |
| 7.1 |
CREATE TABLE |
SELECT INTO |
SELECT |
CREATE TYPE |
ALTER TABLE |
| 7.0 |
SELECT |
SELECT INTO |
CREATE TYPE |
CREATE TABLE |
COMMENT |
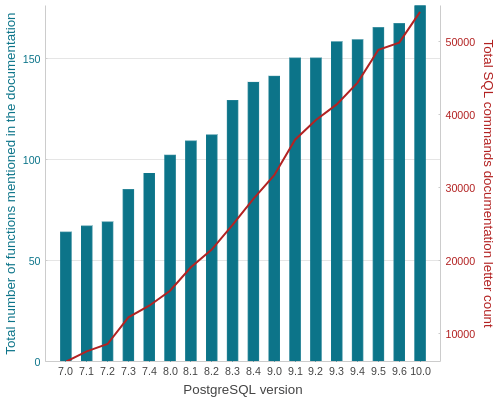
Number of functions available in each version
SELECT
version,
count(func),
sum(letter_count)
FROM postgresql_development.data
GROUP BY version ORDER BY version;
The most verbose docs in each version
SELECT DISTINCT ON (version)
version,
func,
letter_count
FROM postgresql_development.data
ORDER BY version, letter_count DESC;
Poor REVOKE, the defeated champion.
| VERSION |
FUNCTION |
LETTER COUNT |
| 10 |
CREATE TABLE |
3142 |
| 9.6 |
REVOKE |
2856 |
| 9.5 |
REVOKE |
2856 |
| 9.4 |
REVOKE |
2856 |
| 9.3 |
REVOKE |
2856 |
| 9.2 |
REVOKE |
2856 |
| 9.1 |
REVOKE |
2508 |
| 9 |
REVOKE |
2502 |
| 8.4 |
REVOKE |
2105 |
| 8.3 |
REVOKE |
1485 |
| 8.2 |
REVOKE |
1527 |
| 8.1 |
REVOKE |
1312 |
| 8 |
CREATE TABLE |
1251 |
| 7.4 |
CREATE TABLE |
1075 |
| 7.3 |
CREATE TABLE |
929 |
| 7.2 |
CREATE TABLE |
929 |
| 7.1 |
CREATE TABLE |
871 |
| 7 |
SELECT |
450 |
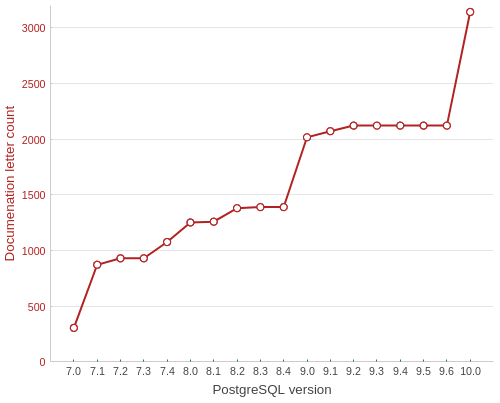
CREATE TABLE docs evolution
SELECT
version,
letter_count
FROM postgresql_development.data
WHERE func = 'CREATE TABLE'
ORDER BY func, version;
Something’s going on in an upcoming 10.0 version.
All the data was obtained with the following Python script and processed inside the PostgreSQL database. Plots done with Bokeh, though I probably wouldn’t use it again, the docs site is absurdly sluggish and the info is just all over the place.